HAHN Automation Group Enhances Precision with Automated Needle Preloading
Bringing a product to market often requires a shift from a manual process to an automated one. In this example, you can learn about how we helped a medical device manufacturer incorporate automation into their once tedious process. We will call this customer "Ava." Ava, an ophthalmic device company, leveraged a manual process for the loading of their ocular drug delivery system, leading to inaccuracies. As demands increased, they needed an automated solution to replace their tabletop process, which yielded only a 40% acceptance rate.
#automation #MedTech #ophthalmic
- Transition from manual to semi-automated process
- Reduced cycle time by over 50%
- Increased repeatability, yielding higher acceptance rate
Challenge
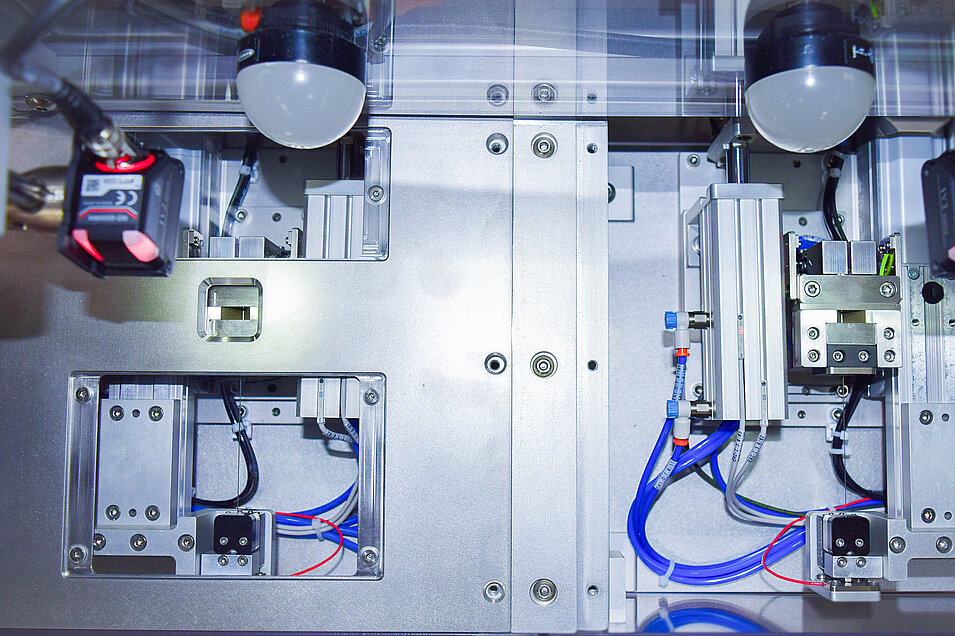
The assembly process involved loading a needle hub assembly with a compact, cylindrical medicine. Due to the dimensions of the needle and the medication, the assembly required a push wire with a diameter of approximately .014,” making it difficult for an operator to handle without damaging the needle or bending the push wire. These dimensions also meant it was hard for the operator to visually confirm that the medicine had been placed into the needle and was in the correct position. With no previous experience leveraging automation equipment, Ava needed a partner who could assess their current process for solutions that would meet their expectations—while staying practical within the boundaries of their budget and operator expertise.
Developing a Solution
Prior to our solution, the assembly was done with an operator-dependent, tabletop assembly station. Because our machine was their first piece of automation, it took collaboration from both sides to work through the best way to introduce equipment into the process. Ultimately we used a semi-automated approach that would minimize operator involvement in order to increase efficiency while providing feedback to confirm accuracy. The resulting system uses a robotic arm and four different sensors throughout the process to indicate the success of each step.